Here is a comprehensive and at the same time a compact detail of penicillin antibiotics including classification, mechanism of action, Clinical uses, reported adverse effects and dosage guidelines. Happy reading !!
Introduction:
Antibiotics that contain β-lactam (a four membered cyclic amide) ring structure constituent the dominant class of agents currently employed for chemotherapy of bacterial infections. Penicillin , cephalosporins, and their semi-synthetic derivatives come under this class.
Classification:
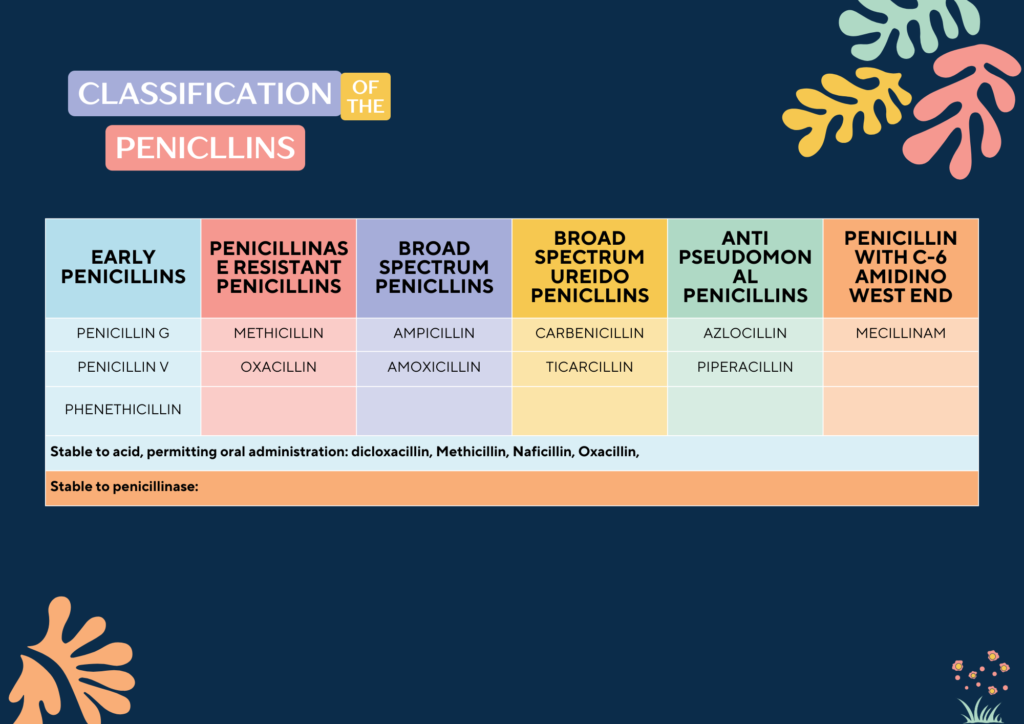
Mechanism of action:
Penicillins, like all beta lactam antibiotics ,interfere in transpeptidation of the bacterial cell wall synthesis, which is responsible for its cell integrity.
(Bacteria defense its specialized rigid cell wall) Bacterial cell wall is composed of a complex, cross linked polymer of polysaccharide and polypeptides (NAG (N-acetyl glucosamine) and NAM (NAG (N-acetyl muramic acid)), to form peptidoglycan. These glycan chains are cross linked by peptide chains which give it rigidity. β-lactam antibiotics structural analog of natural D-Ala-D-Ala substrate covalently bind to the active site of PBPs. This inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis and cell dies. The exact mechanism of cell death is not known but autolysins and disruption of cell wall morphogenesis is involves. . β-lactam antibiotics kill bacteria only when they are actively growing and synthesizing cell wall.
Pharmacokinetics:
- Absorption: Orally administerd penicillin has different absorptions depending on their acid stability and protein binding. GI absorption of naficillin is anomalous, so it is not suitable for oral administration.Dicloxacillin, ampicillin and amoxicillin are acid stable and relatively well absorbed. Producing serum concentration of 4-8 mcg/ml after a 500mg oral dose.
Absorption of most penicillins (amoxicillin being an exception) is impaired by food, and the drugs should be administered at least 1-2 hours before or after a meal.
*protein binding becomes clinically significant when binding percentage is approx. 95% or more.
*Benzathine and procaine penicillins are formulated to delay absorption resulting in prolonged blood and tissue concentrations.
- Distribution: Poor penetration to eye, prostrate and CNS. But in case of inflamed meninges as in meningitis. Penicillins concentration reaches to 1-5 µg/ml by administering 18-24 million units. These concentrations are sufficient to kill strains of meningococci and pneumococci.
- Metabolism: host metabolism of beta lactam antibiotics is usually insignificant.
- Excretion: primary route of secretion is through (tubular) secretory system of kidney as well as glomerular filteration. Patients with impaired renal function must have dose regimen adjusted. Thus half life of penicillin G can increase in presence of renal dysfunction.
Probenecid inhibits the secretion of penicillins by completion with it for active tubular secretion via organic acid transporter and thus can increase in blood levels. Naficillin, dicloxacillin and oxacillin are exceptions not eliminated by kidneys. Penicillins are excreted in breast milk..
Indications:
Therapeutic application of penicillin G:
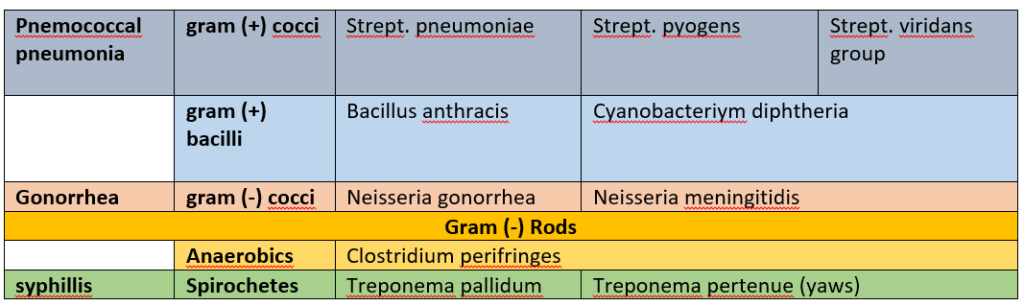
Penicillin G is a drug of choice for infections caused by streptococci, meningococci some enterococci, penicillin susceptible pneumococci, non β lactamase producing staphylococci, treponema pallidum and certain other spirochetes, Clostridium species, actinomyces and certain other gram positive rods and non β lactamase producing gram negative anaerobic organisms.
- Penicillin V (oral form) indicated in minor infections only, due to its narrow spectrum and poor bioavailability, Amoxicillin is used instead.
- Penicillins resistant to staphylococcal beta lactamases (Methicillin, Naficillin Isoxazolyl penicillins):
- indicated for β lactam producing staphylococci
- listeria monocytogeenes, enterococci and methicillin resistant strains of staphylococci are resistant
- Isoxazolyl penicillin such as oxacillin, cloxacillin and dicloxacillin 0.25 to 0.5g orally every 4-6 hrs for mild to moderate localized staphlicoccal infection. moderate bioavailability. However food interferrs with absorption therefore should be administered 1 hour before or after meals.
- For serious systemic staphylococcal infections, oxacillin or naficillin 8-12g/day given by intermittent intravenous infusion of 1-2g every 4-6 hours (50-1—mg/kg/d for children).
- Extended spectrum penicillins (Aminipenicillin, carboxypenicillin, ureidopenicillins):
- Greater gram negative bacteria activity, due to its enhanced ability of penetration in outer membrane.
- Inactivate by many β lactamases.
- Aminopenicllin (amoxicillin and ampicillin) has nearly same spectrum but amoxicillin is preferred due to better oral absorption.
- Amoxicillin 250-500 mg three times daily is equivalent to same dose of ampicillin four times daily.
- Amoxicillin is used to treat UTI, sinusitis, otitis and lower respiratory tract infections.
- Ampicillin (not amoxicillin) is effective against shigellosis.
- Ampicillin 4-12g/day used for treating infections caused by susceptible organisms including anaerobes, enterococci, L.monocytogenes, β lactamase -ve strains of gram –ve cocci and bacilli such as E.coli, salmonella sp. ,strains that are resistant due to altered PBP’s are emerging.
- Many gram –ve strains are resistant and produce beta lactamases precluding use of ampicillin for empirical therapy of UTIs, meningitis and typhoid fever.
- Ampicillin is not active against klebsiella sp, Enterobacter sp., P aeruginose, Citrobactor sp., Serratia marcescens, indole positive proteus species and other gram negative aerobes that are commonly encountered in hospital acquired infections. These organisms produce β lactamase that inactivates ampicillin.
- Ticarcillin is used instead of carbencillin in USA which has same activity.
- An antipseudomonal penicillin is frequently used along with aminoglycoside or fluoroquinolones for pseudomonal infection outside of urinary tract.
- Combination of Ampicillin, amoxicillin, ticarcillin and piperacillin with several β lactamase inhibitors (clavulanic acid, sulbactam or tazobactam) extends their activity to β lactamase producing S. aureus and some β lactamase producing gram –ve bacteria.
Clinical use of Probenecid:
Penicillins levels can be raised by simultaneous use of probenecid 0.5 g (10mg/kg for children) which impairs renal tubular secretion of weak acids such as β lactam compounds.
Guidelines for dosing of some commonly used penicillins:

Adverse effects:
- Hypersensitivity: This is the most important adverse effect of penicillin .(metabolite , penicilloic acid which react with protein serve as hapten to cause immune reaction). Patient shows reaction ranging from rash, angioedema to anaphylaxis.
- Diarrhea: Due to disruption of normal flora of intestine it’s a common problem.
- Nephritis : All penicillin ,particularly methicillin has the potential to cause acute interstitial nephritis.(methicillin is therefore longer available)
- Neurotoxicity: penicillin are irritating to neuronal tissues. If injected intrathecal can cause seizures or if attain very high blood levels. Epileptic patients are particularly at risk.
- Hematologic toxicities: decreased coagulation may occur with high doses of piperacillin, ticarcillin and nafcillin. cytopenia and eosinophilia may also occur therefore CBC is recommended.
- Cation toxicity.
- Drug specific adverse reaction are mentioned as:
- Naficillin › neutropenia
- Oxacillin › hepatitis
- Methacillin › interstitial nephritis
- Penicillin (large doses given orally) › GI upset (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
- Ampicillin › pseudomonal colitis
- Ampicillin & amoxicillin › skin rashes not allergic in nature (frequently occur when inappropriately prescribed for viral illness)
- When a1nd how to take orally for best efficacy:
- Except for amoxicillin most oral penicillins absorption impairs with food therefore they are administered at least 1-2 hours before or after meals.
